The Intriguing Connection Between Jazz and Mental Wellness
Written on
Chapter 1: The Power of Jazz
The classic jazz piece "Take Five" by The Dave Brubeck Quartet captivates listeners from the very first seven seconds. The piano’s soothing tones create an avant-garde soundscape that has a calming effect on the mind. This prompts an intriguing question: how does music affect not just our auditory senses but also our physical well-being and, more specifically, our brain? The science behind this phenomenon is often overlooked. Engaging with music can help alleviate anxiety, calm our nerves, and enhance focus—benefits that should be embraced daily and celebrated.
The title of this article pays homage to a favorite track from the legendary hip-hop group, A Tribe Called Quest, who blended jazz, funk, and soul with hip-hop rhythms. In the song "Jazz (We’ve Got)", Q-Tip lyrically invites listeners to relax and enjoy the music, saying, “Then cool out to the music ’cause it makes you feel serene.” The chorus resonates with the catchy refrain, “We got the jazz, we got the jazz,” accompanied by subtle horn and drum arrangements.
Listening to this iconic track from the 1990s not only makes me nod along but also evokes cherished memories and positive reflections from my youth.

Chapter 2: Understanding the Science of Sound
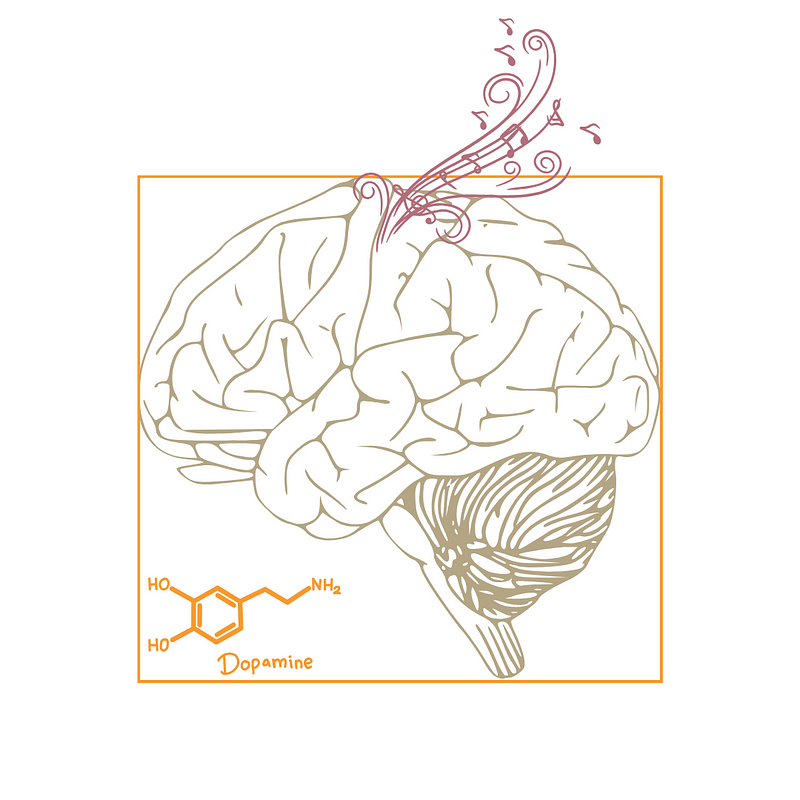
These musical examples illustrate the significant impact that music has on our mental states. Recent research has delved into this topic, revealing that music serves a purpose far beyond mere entertainment. A study titled "Music, Mental Health, and Immunity" highlights that sound can positively influence our mental health, stating: “music can influence physiological processes that enhance physical and mental wellbeing.” It further notes that patients with mental health disorders often show improvement after engaging with music therapy.
Another insightful article, "Your Brain On Music," discusses how various brain regions respond to music. It details how music can affect cognitive functions, reduce stress, and foster positive outcomes. Neuroscientist Kiminobu Sugaya explains that music can activate areas like the Frontal Lobe, enhancing its functions. Additionally, Wernicke’s Area plays a role in our enjoyment and analysis of music.
The research also examines the Nucleus Accumbens, which is associated with reward and pleasure, as well as the Hypothalamus, which regulates feelings of hunger and thirst. Studies suggest that listening to music can influence heart rate and blood pressure.
Chapter 3: Reevaluating Our Relationship with Music
In summary, music can be a potent ally for our mental health—a tool that remains underutilized. While many people listen to music primarily for entertainment, research indicates that it can also help alleviate social stress. The study "The Psychological Functions of Music Listening" emphasizes music's ability to evoke transcendent feelings and enhance our memories, emotions, and overall mood.
Music transcends mere entertainment; it has the potential to support our emotional, social, physiological, and cognitive needs. Regardless of genre—be it jazz, hip-hop, soul, or rock—our brains respond to music without regard to style. So, indulge in your favorite tunes and enjoy the benefits they bring.
To conclude, I echo the sentiments of The O’Jays in their song, “I Love Music”: “I love music, any kind of music, I love music, just as long as it’s groovin’, makes me laugh, makes me smile all the while.”
